Executive Summary
The LP Gas retail business in Zimbabwe presents both opportunities and challenges for aspiring entrepreneurs. While the chronic electricity shortages create substantial demand for LP Gas, stringent price controls by ZERA significantly compress profit margins, making this a challenging venture for small operators. This comprehensive guide examines the complete business model, from startup costs and licensing requirements to realistic profitability projections and supplier networks.
Market Overview and Opportunity
The Energy Crisis Context
Zimbabwe’s persistent electricity crisis has fundamentally altered household energy consumption patterns. Load shedding affects most urban areas daily, with electricity often unavailable during peak cooking hours. The situation is further complicated by:
Urban Development Challenges:
- New residential areas lacking electricity infrastructure
- Delayed utility connections in growing suburbs
- Unreliable grid supply even in established neighborhoods
Consumer Behavior Shifts:
- Households increasingly adopting LP Gas as primary cooking fuel
- Growing demand for portable, reliable energy solutions
- Willingness to pay premium for consistent energy access
Market Size and Growth: The LP Gas market in Zimbabwe has experienced steady growth, driven by both necessity and convenience. Urban penetration rates continue to increase as more households recognize the reliability and efficiency of LP Gas for cooking and heating applications.
Competitive Landscape
The LP Gas retail market consists of several player categories:
Large Integrated Players:
- Service station chains (eg Zuva)
- Vertically integrated suppliers controlling import-to-retail value chain
- Benefit from economies of scale and diversified revenue streams
Independent Wholesalers:
- Import and distribute LP Gas in bulk (eg Quality Gases)
- Often operate their own retail outlets
- Control both wholesale margins and retail profits
Small Independent Retailers:
- Single-outlet operators
- Dependent on wholesaler pricing
- Limited bargaining power but lower overhead costs
Detailed Startup Requirements
Location and Infrastructure
Site Selection Criteria: Choosing the right location is critical for success. Consider these factors:
- High foot traffic areas: Shopping centers, markets, residential hubs
- Accessibility: Easy vehicle access for delivery trucks
- Proximity to competitors: Balance between competition and market density
- Safety considerations: Away from schools, hospitals, and high-risk areas
- Future development plans: Ensure area won’t become restricted
Rental Costs: Rentals for small outdoor retail spaces start from around US$200 per month in busy shopping centers. Can go as high as US$800.
Infrastructure Development: Building a compliant LP Gas retail kiosk requires specific materials and construction standards:
Kiosk Specifications:
- Standard dimensions: 2.5m x 2.4m x 2.1m (can be customized)
- Foundation: Concrete base with proper drainage
- Framework: Deformed bars, angle iron, square tubing
- Roofing: Fire-resistant sheets
- Ventilation: Adequate airflow to prevent gas accumulation
- Security features: Lockable storage, security lighting
Construction Cost: A local welder can construct a basic structure from US$350 – US$700 depending on the size, inclusive of both labour and materials.
Equipment and Machinery
Storage Cylinders (48kg capacity):

- Second-hand cylinders cost approximately US$90
- Brand-new cylinders range from US$150 and upwards
Pumping Equipment:
- Manual pumps and DC pumps (which can run on solar) are often preferred over electric pumps due to load shedding
- Prices for new pumps start at about US$250, depending on brand, capacity, and speed
Weighing Equipment:

- Accurate scales cost from US$35 each
- You should have at least two scales
Staffing:
- At least one employee will be required to operate the outlet
- Salaries starting from US$150 per month, excluding transport and food allowances
Comprehensive Licensing Guide
Step-by-Step Licensing Process
The licensing process involves multiple regulatory bodies and can take 1 month to complete:
Phase 1: Local Authority Approval
Required Documents:
- Company registration certificate
- Memorandum and Articles of Association
- Lease agreement or property ownership documents
- Site plan (professionally drawn)
- Floor plan showing layout and safety features
- Director’s national IDs and proof of residence
Departmental Assessments:
- Town Planning Department: Verifies zoning compliance and land use appropriateness
- Fire Department: Inspects safety measures, fire prevention systems, and emergency access
- Environmental Department: Assesses environmental impact and waste management plans
Phase 2: Environmental Management Agency (EMA) Clearance
After receiving approval from the local authority, the next step is obtaining clearance from the Environmental Management Agency (EMA). This requires company documents and a site inspection to ensure environmental compliance.
Phase 3: ZERA Licensing
Once you have EMA approval, you proceed to ZERA, which will require your company documents along with proof of local authority and EMA approvals. If successful, ZERA will issue your LP Gas licence.
Total Licensing Costs
The total cost for all required licences is approximately US$600.
Financial Analysis and Projections
Financial Analysis and Projections
Startup Capital Requirements: Taking into account the basic setup, equipment, and initial stock, you should budget a minimum of US$2,000 to get started, excluding licensing costs.
Understanding the Financials
LP Gas wholesalers are currently selling LP Gas at US$1.25 per kilogram, while ZERA’s current gazetted maximum retail price is US$1.51 per kilogram. This means you are legally prohibited from charging more than this price. If you operate strictly within the legal framework, your gross profit margin is $1.51-$1.25 = US$0.26 per kilogram.
From this margin, you must subtract transport costs, which is why it is advisable to have as many storage tanks as possible to minimise trips to the wholesaler. Transport costs vary depending on your distance from the supplier. Typically, you will hire a small truck, load your cylinders, travel to the wholesaler to fill them, and then return. If you are located near the wholesaler, you may pay around US$15 for transport.
For example, if you have four 48kg tanks, you will be purchasing a total of 192 kilograms. This results in a transport cost of US$15 ÷ 192 = approximately US$0.08 per kilogram. Subtracting this from the US$0.26 gross margin leaves you with an effective profit margin of US$0.18 per kilogram.
Industry operators note that, although you purchase 48 kilograms, some stock loss occurs during selling and handling, and you may end up selling closer to 45 kilograms or less. For the purpose of this analysis, we will disregard that factor.
At a US$0.18 margin, you must sell large volumes to achieve meaningful profits. If you manage to sell 150 kilograms per day (which is optimistic for small players), your daily profit would be 150 × US$0.18 = US$27. Over a 30-day month, that amounts to US$810 gross profit before operating expenses. From this figure, you still need to deduct rent, salaries, stock loss, and other operating costs. You will end up with US$400 or less.
It is clear that this is a challenging business, particularly for small operators without high sales volumes or an exceptional location.
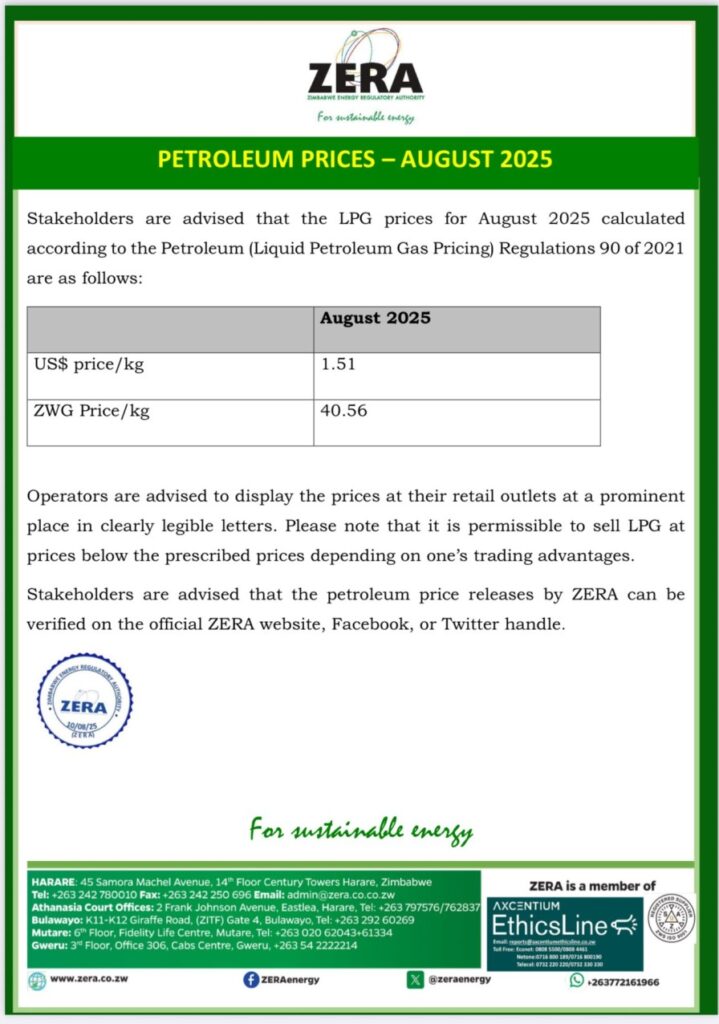
Pricing Structure:
- LP Gas wholesalers are currently selling LP Gas at US$1.25 per kilogram
- ZERA’s current gazetted maximum retail price is US$1.51 per kilogram [as of August 2025]
- Gross profit margin: US$0.26 per kilogram
Transport Costs Example: Transport costs vary depending on your distance from the supplier. If you have four 48kg tanks (192 kilograms total) and transport costs US$15, this results in a transport cost of approximately US$0.08 per kilogram.
Net Profit Margin: Subtracting transport costs from the gross margin leaves you with an effective profit margin of US$0.18 per kilogram.
Profitability Example: If you manage to sell 150 kilograms per day, your daily profit would be 150 × US$0.18 = US$27. Over a 30-day month, that amounts to US$810 gross profit before operating expenses. After deducting rent, salaries, stock loss, and other operating costs, you will end up with US$400 or less.
Market Realities and Challenges
Price Control Impact
ZERA’s price controls create several challenges for retailers:
Margin Compression:
- ZERA prices results in low profit margin
- Limited ability to pass on cost increases
- Squeezed profits during periods of rising wholesale prices
Competitive Disadvantages:
- Legal operators compete with unlicensed vendors who ignore price controls
- Pressure to cut costs through potentially unsafe practices
- Difficulty maintaining service quality with razor-thin margins
Unethical Practices in the Industry
While we strongly advise against these practices, it’s important to understand what some operators resort to:
Unethical Practices: Some operators choose to disregard ZERA’s price controls, selling LP Gas at US$1.75+, although doing so carries the serious risk of having their licence revoked. Others operate without a licence altogether, avoiding regulatory compliance entirely.
There are also those who manipulate the calibration of their scales so that what is sold as 1KG is actually closer to 900 grams. While this practice is unethical, some argue that it is the only way to keep their businesses afloat given the tight margins.
Success Factors for Ethical Operations
Volume-Based Success: Achieving profitability while operating legally requires focus on:
- Location optimization: High-traffic areas with minimal competition
- Customer service excellence: Building loyalty and repeat business
- Operational efficiency: Minimizing waste and optimizing processes
- Cost management: Negotiating better wholesale prices, reducing transport costs
Diversification Strategies: Successful operators often expand beyond basic LP Gas sales:
- Equipment sales: Cylinders, regulators, hoses, stoves
- Appliance retail: Heaters, cookers, and LP Gas-powered equipment
- Maintenance services: Equipment repairs and safety inspections
- Delivery services: Home and business delivery for premium customers
Equipment and Accessories Business
Supplementing Income Through LP Gas Equipment

In addition to selling LP Gas itself, you can increase your revenue by offering related equipment and accessories. These include gas cylinders of various sizes, regulators, hoses, stoves, heaters, and other appliances that use LP Gas. Many customers prefer the convenience of purchasing their gas and equipment from the same place, especially when setting up for the first time or replacing worn-out items. By stocking and selling these products, you not only diversify your income streams but also position your business as a one-stop solution for LP Gas needs, which can help build customer loyalty and increase repeat business.
LP Gas Retail Business Plan Template
Executive Summary Template
When developing your business plan, include the following key elements:
Business Overview:
- Business name and legal structure
- Location and target market description
- Mission statement and business objectives
- Unique value proposition
Financial Highlights:
- Total startup investment required
- Projected monthly sales volumes
- Expected profitability timeline
- Break-even analysis
Success Factors:
- Strategic location advantages
- Competitive positioning
- Management experience and qualifications
Market Analysis Section
Market Research Components:
Local Market Assessment:
- Population density and demographics in your area
- Number of households without reliable electricity
- Current LP Gas usage patterns and preferences
- Seasonal demand variations
Competitive Analysis:
- Identify existing LP Gas retailers within 5km radius
- Analyze their pricing, service levels, and market share
- Assess their strengths and weaknesses
- Identify market gaps and opportunities
Target Customer Profile:
- Primary customers: Urban households affected by load shedding
- Secondary customers: New residential developments
- Commercial customers: Small restaurants, hair salons, informal businesses
- Customer purchasing patterns and volume requirements
Operational Plan
Location Strategy:
- Site selection criteria and rationale
- Lease terms and rental costs
- Proximity to target customers and suppliers
- Traffic patterns and accessibility
Facility Requirements:
- Kiosk specifications and construction timeline
- Storage capacity and layout design
- Safety equipment and compliance measures
- Security systems and procedures
Supply Chain Management:
- Primary and backup suppliers identification
- Delivery schedules and inventory management
- Quality control procedures
- Supplier relationship management
Staffing Plan:
- Job descriptions and qualifications required
- Training programs and safety procedures
- Compensation structure and performance incentives
- Supervision and management protocols
Financial Projections
Startup Costs Breakdown: Detail your specific costs for:
- Site preparation and kiosk construction
- Equipment and storage cylinders
- Initial inventory investment
- Working capital for first three months
- Licensing and permit costs
Revenue Projections: Develop realistic sales forecasts based on:
- Daily sales volume targets (conservative, moderate, optimistic scenarios)
- Seasonal variations and market trends
- Equipment and accessories sales potential
- Growth projections for years 1-3
Operating Expenses: Monthly fixed and variable costs including:
- Rent and utilities
- Staff salaries and benefits
- Transport and delivery costs
- Insurance and licensing renewals
- Marketing and promotional expenses
Profitability Analysis:
- Monthly break-even volume calculations
- Gross and net profit margin projections
- Cash flow forecasts for first 12 months
- Return on investment timeline
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Business Risk Factors:
- Regulatory changes affecting pricing or licensing
- Supply chain disruptions or price volatility
- Increased competition or market saturation
- Economic downturns affecting customer spending
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
- Diversification through equipment sales
- Building strong supplier relationships
- Maintaining adequate cash reserves
- Insurance coverage and safety protocols
Contingency Planning:
- Alternative supplier arrangements
- Emergency response procedures
- Business continuity during disruptions
- Exit strategy considerations
Marketing and Customer Acquisition
Marketing Strategy:
- Grand opening promotions and community engagement
- Customer loyalty programs and repeat business incentives
- Referral programs and word-of-mouth marketing
- Local advertising and partnership opportunities
Customer Service Standards:
- Service quality benchmarks
- Customer complaint resolution procedures
- Feedback collection and improvement processes
- Community involvement and reputation building
Growth and Expansion Plans
Short-term Goals (Year 1):
- Achieve break-even within specified timeframe
- Build customer base and market recognition
- Establish efficient operations and cash flow
- Meet all regulatory compliance requirements
Medium-term Goals (Years 2-3):
- Expand equipment and accessories offerings
- Consider additional service offerings
- Evaluate second location opportunities
- Develop commercial and institutional customers
Long-term Vision (Years 3-5):
- Multiple location operations
- Vertical integration opportunities
- Partnership or franchise development
- Market leadership positioning
Implementation Timeline
Pre-Launch Phase (Months 1-3):
- Secure financing and location
- Complete licensing and regulatory approvals
- Construct facility and install equipment
- Hire and train initial staff
Launch Phase (Month 4):
- Grand opening and initial marketing campaign
- Begin operations and customer acquisition
- Monitor performance and adjust operations
- Build supplier relationships and inventory systems
Growth Phase (Months 5-12):
- Optimize operations and cost management
- Expand product offerings and services
- Evaluate performance against projections
- Plan for expansion or improvements
Financial Controls and Monitoring
Key Performance Indicators:
- Daily and monthly sales volumes
- Profit margins and cost control metrics
- Customer acquisition and retention rates
- Inventory turnover and stock management
Financial Management:
- Daily cash flow monitoring
- Monthly financial statement preparation
- Quarterly performance reviews and adjustments
- Annual business plan updates and strategic planning
Record Keeping Requirements:
- Sales and inventory tracking systems
- Regulatory compliance documentation
- Financial records and tax preparation
- Insurance and safety incident reporting
Conclusion and Next Steps
Your business plan should conclude with specific action items and milestones for moving forward. Include timelines for securing financing, obtaining licenses, and launching operations. Regular review and updating of your business plan will help ensure you stay on track to achieve your goals while adapting to changing market conditions.
Remember that a solid business plan serves not only as a roadmap for your operations but also as a tool for securing financing, partnerships, and regulatory approvals. Take time to research thoroughly and develop realistic projections based on actual market conditions and your specific circumstances.
Strategic Recommendations
For Small Independent Operators
Focus Areas:
- Location is paramount: Invest in the best location you can afford
- Customer relationships: Build loyalty through excellent service
- Cost control: Minimize transport costs through efficient restocking
- Diversification: Add equipment sales to boost margins
- Legal compliance: Avoid shortcuts that could jeopardize the business
Risk Mitigation:
- Maintain adequate insurance coverage
- Keep detailed financial records
- Stay updated on regulatory changes
- Build relationships with reliable suppliers
- Plan for seasonal demand fluctuations
For Potential Investors
Key Considerations:
- Conduct thorough market research in your target area
- Analyze local competition and pricing
- Verify all regulatory requirements and costs
- Assess transportation logistics and costs
- Evaluate potential locations carefully
- Consider partnering with experienced operators
Growth and Expansion Strategies
Vertical Integration Opportunities:
- Partner with wholesalers for better pricing
- Develop delivery and installation services
- Expand into commercial and industrial markets
- Consider cylinder refurbishment services
Horizontal Expansion:
- Multiple retail locations
- Franchise or partnership models
- Online ordering and delivery platforms
- Corporate and institutional supply contracts
Supplier Directory and Partnerships
The supplier contact details provided in this guide are for informational purposes only. ZimLedger does not have any affiliation with these suppliers, nor do we endorse or guarantee the quality, pricing, or reliability of their products and services. It is the responsibility of the reader to conduct due diligence before engaging with any supplier, including verifying their credentials, pricing, and compliance with relevant regulations.
LP Gas Wholesalers
Quality Gases
- Contact: +263 788 707 707; +263 788 707 100
- Services: Wholesale LP Gas, equipment supply
Pandi Gas
- Contact: +263 771 828 133; +263 771 833 759
- Services: LP Gas wholesale, cylinder supply
Equipment Suppliers
T & C Gas Equipment and Accessories
- Contact: +263 775 185 263; +263 242 706 785
- Specialization: Complete equipment range
- Services: Installation and maintenance support
Lucky Planet Gas Equipment And Accessories
- Contact: +263 714 803 963; +263 777 047 788
- Focus: Complete equipment range
- Advantage: Installation and maintenance support
Nexas Gas & Equipment
- Contact: +263 777 378 095; +263 776 515 680; +263 783 613 445; +263 783 613 481
- Services: Equipment supply, technical support
- Coverage: Nationwide delivery network
Alternative Sourcing Options
Local Hardware Stores
- Competitive pricing on basic equipment
- Immediate availability
- Limited technical support
Facebook Marketplace and Online Platforms
- Second-hand equipment options
- Direct supplier connections
- Price comparison opportunities
- Due diligence required for quality assurance
Supplier Relationship Management
Key Relationship Factors:
- Payment terms: Negotiate favorable credit arrangements
- Delivery schedules: Ensure reliable supply chains
- Technical support: Access to maintenance and repair services
- Volume discounts: Negotiate better pricing for larger orders
- Training programs: Staff training on new equipment
Supplier Evaluation Criteria:
- Reliability and consistency of supply
- Competitive pricing and payment terms
- Technical support and after-sales service
- Compliance with safety and quality standards
- Financial stability and market reputation
Risk Management and Safety
Business Risks
Operational Risks:
- Equipment failure and downtime
- Supply chain disruptions
- Staff safety incidents
- Customer accidents on premises
Financial Risks:
- Price control changes affecting margins
- Wholesale price volatility
- Seasonal demand fluctuations
Regulatory Risks:
- License revocation or suspension
- New compliance requirements
- Penalty costs for violations
Market Risks:
- New competition entering the market
- Customer preference changes
- Economic downturns affecting demand
Future Outlook and Industry Trends
Market Growth Drivers
Urbanization and Development:
- Continued urban expansion creating new markets
- Infrastructure development in peri-urban areas
- Growing middle-class adoption of LP Gas
Energy Sector Challenges:
- Persistent electricity supply issues
- Rising electricity costs
- Government focus on energy diversification
Consumer Awareness:
- Increasing awareness of LP Gas benefits
- Environmental consciousness driving cleaner fuel adoption
- Convenience and reliability preferences
Technology and Innovation Trends
Digital Solutions:
- Mobile payment integration
- Delivery tracking and scheduling apps
- Inventory management systems
- Customer loyalty programs
Equipment Improvements:
- More efficient and safer appliances
- Smart gas monitoring systems
- Improved cylinder and valve designs
- Enhanced safety features
Regulatory Evolution
Expected Changes:
- Potential price control modifications
- Enhanced safety and environmental standards
- Digital licensing and compliance systems
- Consumer protection improvements
Industry Standardization:
- Equipment quality standards
- Service delivery benchmarks
- Professional certification requirements
- Industry best practice guidelines
Conclusion and Final Recommendations
The LP Gas retail business in Zimbabwe presents a mixed picture of opportunity and challenge. While market demand remains strong due to energy sector constraints, regulatory price controls and operational complexities make profitability challenging for small operators.
Key Success Factors
Critical for Profitability:
- High-volume sales
- Prime location with high foot traffic and minimal competition
- Operational efficiency to minimize costs and maximize margins
- Diversified revenue streams through equipment and accessory sales
- Strict legal and ethical compliance to ensure long-term sustainability
Strategic Advice
For Prospective Entrepreneurs:
- Conduct thorough market research and financial planning
- Secure adequate startup capital with 6-month operating reserves
- Choose location carefully based on traffic and competition analysis
- Build relationships with reliable suppliers and maintain good credit terms
- Focus on customer service excellence to build loyalty and repeat business
For Existing Businesses:
- Evaluate current profitability and consider diversification strategies
- Invest in equipment sales and service capabilities
- Optimize operations to reduce costs and improve efficiency
- Stay compliant with all regulatory requirements
- Plan for potential market and regulatory changes
Final Word
Success in the LP Gas retail business requires realistic expectations, careful planning, and disciplined execution. While the business can be profitable under the right circumstances, it is not a guaranteed path to wealth. Those considering entry should carefully evaluate their financial capacity, market understanding, and commitment to legal and ethical operations.
The most successful operators combine strategic location selection, operational excellence, customer service focus, and diversified revenue streams while maintaining strict compliance with all regulatory requirements. For those who can meet these demands, the LP Gas retail business can provide a sustainable income stream in Zimbabwe’s challenging economic environment.
ZimLedger
ZimLedger is the all in one business and finance platform for Zimbabwe. It generates quotes, invoices, payslips and financial statements, manages business ledgers, tracks income and expenses, and builds shopping lists. ZimLedger offers a simple yet powerful solution tailored to local needs. Whether you are budgeting in ZiG or USD, managing business accounts, converting Ecocash statements, or tracking household expenses, ZimLedger empowers you to stay organised, make informed financial decisions, and grow your wealth—right from your phone or computer.













